CBIS LM Core: Abberior STEDYCON

Location: CBIS Light Microscopy Core (S1A #01-04 CBIS lab)
Booked CBIS equipment before? Information for First Time Users
Stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy is a super-resolution technique that uses a doughnut-shaped laser beam of long wavelength to deplete the fluorescence signal to a tiny spot in the middle of the doughnut.
The higher the depletion laser power, the smaller the spot and the higher the resolution, but it causes more photodamage.
Images are super-resolution straight out of the microscope and do not require post-processing. However, deconvolution can be performed to further enhance resolution if desired.
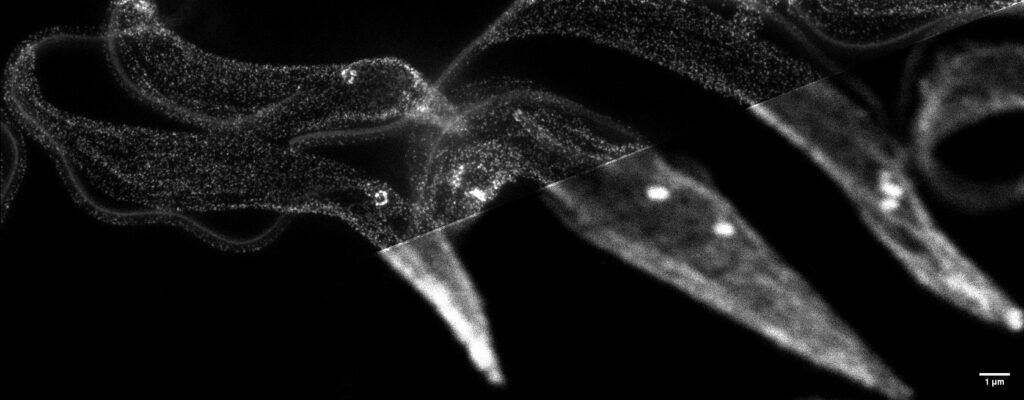 Trypanosoma brucei (STED versus confocal). Sample preparation: Assoc Prof Cynthia He, Principal Investigator, Molecular and Cellular Parasitology Lab, NUS; imaging: Tong Yan, CBIS Light Microscopy Core.
Trypanosoma brucei (STED versus confocal). Sample preparation: Assoc Prof Cynthia He, Principal Investigator, Molecular and Cellular Parasitology Lab, NUS; imaging: Tong Yan, CBIS Light Microscopy Core.
User guides
Features
- Olympus IX81 inverted microscope
- Olympus UPLXAPO 100x/1.45 Oil objective for STED
-
Other objectives:
- Olympus UPLNSAPO 10x/0.40 Air
- Olympus UAPO N 20x/0.70 Water
- Olympus UPlanSApo 20x/0.75 Air
- Olympus PlanAPO N OSC2 60x/1.4, WD 0.12 (super chromatic aberration correction, compensation range 405-650nm)
- Universal sample holder for slides, dishes and plates
- Continuous autofocus
- Confocal and STED with time gating
- Excitation lasers 405, 488, 561, 640 nm
- STED laser 775 nm pulsed
- Piezo z scanner
- Four APD detectors
- Detection bands 420-480, 505-550, 575-625, 650-700 nm
- Field of view up to 90 μm x 80 μm
- Frame rate up to 1.1 fps at 512 x 512 pixels
- Multiposition and tiling currently unavailable
- Outputs raw photon count data openable in Fiji as 16-bit image
